C库的内存分配函数void *realloc(void *ptr, size_t size) 尝试重新调整由ptr指向的先前使用malloc或calloc调用分配的内存块。
内存可以通过以下两种方式进行分配:
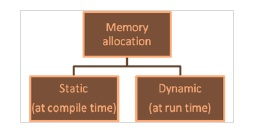
一旦在编译时分配了内存,就无法在执行期间更改。要么内存不足,要么内存浪费。
解决方案是动态创建内存,即根据程序在执行期间的需求。
用于动态内存管理的标准库函数如下:
用于重新分配已经分配的内存。
可以减少或增加已分配的内存。
返回一个指向重新分配内存的基地址的void指针。
realloc()函数的语法如下:
Free void *realloc (pointer, newsize);
以下示例展示了realloc()函数的用法。
int *ptr; ptr = (int * ) malloc (1000);// we can use calloc also - - - - - - - - - ptr = (int * ) realloc (ptr, 500); - - - - - - ptr = (int * ) realloc (ptr, 1500);
下面是使用realloc()函数的C程序:
在线演示
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
int main(){
int *ptr, i, num;
printf("array size is 5");
ptr = (int*)calloc(5, sizeof(int));
if(ptr==NULL){
printf("Memory allocation failed");
exit(1); // exit the program
}
for(i = 0; i < 5; i++){
printf("enter number at %d: ", i);
scanf("%d", ptr+i);
}
printf("
Let's increase the array size to 7
");
ptr = (int*)realloc(ptr, 7 * sizeof(int));
if(ptr==NULL){
printf("Memory allocation failed");
exit(1); // exit the program
}
printf("
enter 2 more integers
");
for(i = 5; i < 7; i++){
printf("Enter element number at %d: ", i);
scanf("%d", ptr+i);
}
printf("
result array is:
");
for(i = 0; i < 7; i++){
printf("%d ", *(ptr+i) );
}
return 0;
}
当上述程序被执行时,它产生以下结果 −
array size is 5 enter number at 0: 23 enter number at 1: 12 enter number at 2: 45 enter number at 3: 67 enter number at 4: 20 Let's increase the array size to 7 enter 2 more integers Enter element number at 5: 90 Enter element number at 6: 60 result array is: 23 12 45 67 20 90 60





