线程池的原理如下图:
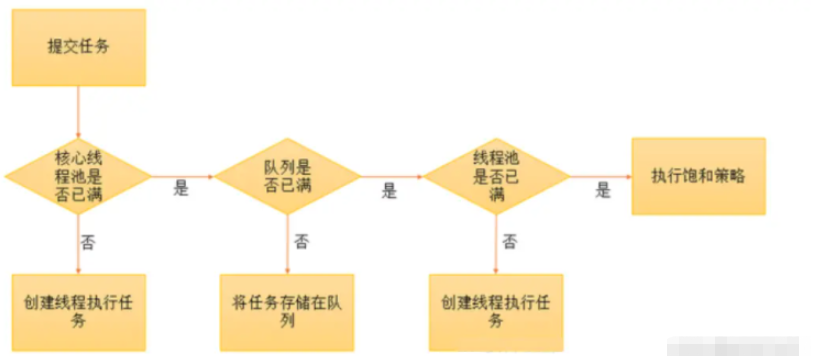
说明:
当前运行的线程少于corePoolSize,则创建新线程来执行任务。
运行的线程等于或多于corePoolSize,则将任务添加到队列中。
当任务队列已满,则在非corePool中创建新的线程来处理任务。
创建新线程将使当前运行的线程超出maximumPoolSize,任务将被拒绝,并调用RejectedExecutionHandler.rejectedExecution()方法。
线程池为我们提供了四种拒绝策略分别是:CallerRunsPolicy,AbortPolicy,DiscardPolicy,DiscardOldestPolicy
ThreadPoolExecutor中默认的拒绝策略就是AbortPolicy直接抛出异常,具体实现如下
public static class AbortPolicy implements RejectedExecutionHandler {
public AbortPolicy() { }
public void rejectedExecution(Runnable r, ThreadPoolExecutor e) {
throw new RejectedExecutionException("Task " + r.toString() +
" rejected from " +
e.toString());
}
}说明:这种策略非常简单粗暴,直接抛出RejectedExecutionException异常,也不会执行后续的任务。
示例说明:
public class ThreadPoolTest
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
ThreadPoolExecutor threadPoolExecutor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(
2,
5,
10,
TimeUnit.MICROSECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingDeque<>(1),
new ThreadPoolExecutor.AbortPolicy());
//异步执行
for(int i=0; i<10;i++)
{
System.out.println("添加第"+i+"个任务");
threadPoolExecutor.execute(new TestThread("线程"+i));
}
}
}
public class TestThread implements Runnable
{
private String name;
public TestThread(String name){
this.name=name;
}
@Override
public void run()
{
try
{
Thread.sleep(1000);
}
catch (InterruptedException e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("thread name:"+Thread.currentThread().getName()+",执行:"+name);
}
}执行结果:
Exception in thread "main" java.util.concurrent.RejectedExecutionException: Task com.skywares.fw.juc.thread.TestThread@55f96302 rejected from java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor@3d4eac69[Running, pool size = 5, active threads = 5, queued tasks = 1, completed tasks = 0]
at java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor$AbortPolicy.rejectedExecution(ThreadPoolExecutor.java:2047)
at java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor.reject(ThreadPoolExecutor.java:823)
at java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor.execute(ThreadPoolExecutor.java:1369)
at com.skywares.fw.juc.thread.ThreadPoolTest.main(ThreadPoolTest.java:26)
thread name:pool-1-thread-5,执行:线程5
thread name:pool-1-thread-2,执行:线程1
thread name:pool-1-thread-4,执行:线程4
thread name:pool-1-thread-3,执行:线程3
thread name:pool-1-thread-1,执行:线程0
thread name:pool-1-thread-5,执行:线程2
从执行结果我们得知,采用AbortPolicy策略当任务执行到第七个任务时会直接报错,导致后续的业务逻辑不会执行。
CallerRunsPolicy在任务被拒绝添加后,会用调用execute函数的上层线程去执行被拒绝的任务。
相关示例
public class ThreadPoolTest
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
ThreadPoolExecutor threadPoolExecutor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(
2,
5,
10,
TimeUnit.MICROSECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingDeque<>(1),
new ThreadPoolExecutor.CallerRunsPolicy());
//异步执行
for(int i=0; i<10;i++)
{
System.out.println("添加第"+i+"个任务");
threadPoolExecutor.execute(new TestThread("线程"+i));
}
}
}执行结果:
添加第0个任务
添加第1个任务
添加第2个任务
添加第3个任务
添加第4个任务
添加第5个任务
添加第6个任务
thread name:main,执行:线程6
thread name:pool-1-thread-3,执行:线程3
thread name:pool-1-thread-1,执行:线程0
thread name:pool-1-thread-4,执行:线程4
thread name:pool-1-thread-2,执行:线程1
thread name:pool-1-thread-5,执行:线程5
添加第7个任务
添加第8个任务
thread name:main,执行:线程8
thread name:pool-1-thread-1,执行:线程7
thread name:pool-1-thread-3,执行:线程2
添加第9个任务
thread name:pool-1-thread-1,执行:线程9
从执行的结果我们可以得知,当执行到第7个任务时,由于线程池拒绝策略,此任务由主线程来执行,当线程池有空闲时,才继续执行其他的任务。所以此策略可能会阻塞主线程。
这种拒绝策略比较简单,线程池拒绝的任务直接抛弃,不会抛异常也不会执行
修改上述的代码,将拒绝策略修改为DiscardPolicy
ThreadPoolExecutor threadPoolExecutor = new ThreadPoolExecutor( 2, 5, 10, TimeUnit.MICROSECONDS, new LinkedBlockingDeque<>(1), new ThreadPoolExecutor.CallerRunsPolicy());
invoke dealStock success
goodsId:手机
thread name:pool-1-thread-1,执行:线程0
thread name:pool-1-thread-4,执行:线程4
thread name:pool-1-thread-5,执行:线程5
thread name:pool-1-thread-3,执行:线程3
thread name:pool-1-thread-2,执行:线程1
thread name:pool-1-thread-1,执行:线程2
从执行的结果来看只执行了6个任务,其他的任务都被抛弃了。
DiscardOldestPolicy 当任务拒绝添加时,会抛弃任务队列中最先加入队列的任务,再把新任务添加进去。
ThreadPoolExecutor threadPoolExecutor = new ThreadPoolExecutor( 1, 2, 10, TimeUnit.MICROSECONDS, new LinkedBlockingDeque<>(2), new ThreadPoolExecutor.CallerRunsPolicy());
执行结果:
添加第0个任务
添加第1个任务
添加第2个任务
添加第3个任务
添加第4个任务
添加第5个任务
invoke dealStock success
goodsId:手机
thread name:pool-1-thread-2,执行:线程3
thread name:pool-1-thread-1,执行:线程0
thread name:pool-1-thread-1,执行:线程2
thread name:pool-1-thread-2,执行:线程1
当线程池提供的拒绝策略无法满足要求时,我们可以采用自定义的拒绝策略,只需要实现RejectedExecutionHandler接口即可
public class CustRejectedExecutionHandler implements RejectedExecutionHandler
{
@Override
public void rejectedExecution(Runnable r, ThreadPoolExecutor executor)
{
new Thread(r,"线程:"+new Random().nextInt(10)).start();
}
}
ThreadPoolExecutor threadPoolExecutor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(
1,
2,
10,
TimeUnit.MICROSECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingDeque<>(2),
new CustRejectedExecutionHandler());执行结果:
thread name:客户线程:6,执行:线程5
thread name:pool-1-thread-1,执行:线程0
thread name:客户线程:8,执行:线程4
thread name:pool-1-thread-2,执行:线程3
thread name:pool-1-thread-1,执行:线程1
thread name:pool-1-thread-2,执行:线程2
从执行的结果来看,被拒绝的任务都在客户的新线程中执行。
AbortPolicy:直接抛出异常,后续的任务不会执行
CallerRunsPolicy:子任务执行的时间过长,可能会阻塞主线程。
DiscardPolicy:不抛异常,任务直接丢弃
DiscardOldestPolicy;丢弃最先加入队列的任务





