1、对属性进行封装,使用户不能直接输入数据,我们需要避免用户再使用"对象.属性"的方式对属性进行赋值。则需要将属性声明为私有的(private).
2、我们将类的属性私有化(private),同时,提供公共的(public)方法来获取(getXxx)和设置(setXxx)此属性的值
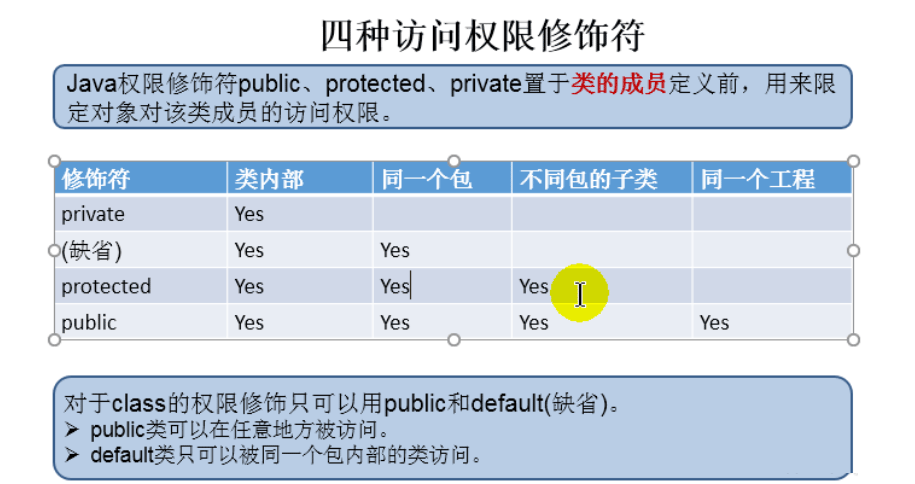
封装性的体现,需要权限修饰符来配合
1.Java规定的4种权限(从小到大排列):private、缺省、protected 、public
2.这4种权限可以用来修饰类及类的内部结构:属性、方法、构造器、内部类
3.具体的,4种权限都可以用来修饰类的内部结构:属性、方法、构造器、内部类
修饰类的话,只能使用:缺省、public
例:
package KindMethod3;
public class privateTest {
// 用private修饰,定义为私有变量,外不不能随意更改
private int age; //年龄
private String name; //名字
// 同时,我们给这两个属性创建两个可以更改他们的接口
public void setAge(int age){
this.age=age;
}
public int getAge(){
return age;
}
public void setName(String name){
this.name=name;
}
public String getName(){
return name;
}
public void disPlay(){
System.out.println("我的名字叫"+name+"今年"+age+"岁");
}
}package KindMethod3;
public class privateTest1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
privateTest sc = new privateTest();
// 这个时候就不能直接给类中属性直接赋值了,就会报错
// sc.age=18;
// sc.name="小芳"
// 我们需要通过set方法给属性赋值,get取值
sc.setAge(18);
sc.setName("小芳");
sc.disPlay();
}
}
一下代码查看运行结果:
public class Order {
private int text1;
int text2;
public int text3;
private void methodPrivate(){
text1 = 1;
text2 = 2;
text3 = 3;
}
void methodDefault(){
text1 = 1;
text2 = 2;
text3 = 3;
}
public void methodPublic(){
text1 = 1;
text2 = 2;
text3 = 3;
}
} public class OrderTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Order order = new Order();
order.text2 = 1;
order.text3 = 2;
//出了Order类之后,私有的结构就不可以调用了
// order.text1 = 3;//The field Order.text1 is not visible
order.methodDefault();
order.methodPublic();
//出了Order类之后,私有的结构就不可以调用了
// order.methodPrivate();//The method methodPrivate() from the type Order is not visible
}
}





