需要具备的知识
Socket网络编程
反向代理的理解
平滑加权轮询算法的理解
线程池的理解
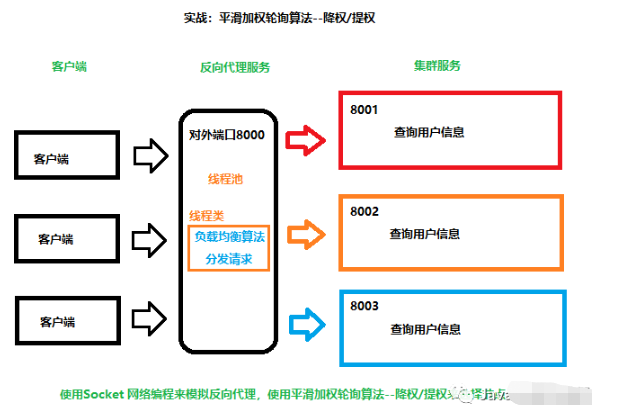
目的:实现Socket 集群服务的平滑加权轮询负载。
业务实现:客户端通过用户名来查询集群服务中的用户信息。
客户端发起Socket请求给反向代理的Socket服务(客户端并不知道服务端是反向代理服务器)
反向代理服务器接收到Socket服务请求
线程池开启服务线程去处理请求
线程服务通过平滑加权轮询算法寻找当前权重最高的下游服务
通过负载均衡算法返回的服务节点信息来创建Socket请求
反向代理服务器使用客户端信息,发起Socket请求给下游服务
Socket集群服务节点收到Socket请求,查询用户信息,再将处理结果返回给反向代理服务器
反向代理服务器再将结果返回给客户端。
几个细节点
使用反向代理服务,对客户端无感,客户端并不知道具体访问了哪个真实服务器;
反向代理服务器每次访问下游服务失败时,就会降低该下游服务器器的有效权重;每次访问下游服务成功时,就会提高该下游服务器的有效权重(不超过配置的权重值);
平滑加权轮询算法会对宕机服务降权和提权,起到”剔除“宕机服务和缓冲恢复宕机服务的效果;
反向代理服务器重启后,所有配置恢复为配置参数;
反向代理服务器使用线程池发布Socket服务,支持多个客户端同时请求同时分发。
用于保存服务节点相关信息
package com.yty.proxy.lba;
public class Node implements Comparable<Node>{
private String ip;
private Integer port;
private final Integer weight;
private Integer effectiveWeight;
private Integer currentWeight;
// 默认权重为:1
public Node(String ip,Integer port){
this(ip,port,1);
}
public Node(String ip,Integer port, Integer weight){
this.ip = ip;
this.port = port;
this.weight = weight;
this.effectiveWeight = weight;
this.currentWeight = weight;
}
public String getIp() {
return ip;
}
public void setIp(String ip) {
this.ip = ip;
}
public Integer getPort() {
return port;
}
public void setPort(Integer port) {
this.port = port;
}
public Integer getWeight() {
return weight;
}
public Integer getEffectiveWeight() {
return effectiveWeight;
}
public void setEffectiveWeight(Integer effectiveWeight) {
this.effectiveWeight = effectiveWeight;
}
public Integer getCurrentWeight() {
return currentWeight;
}
public void setCurrentWeight(Integer currentWeight) {
this.currentWeight = currentWeight;
}
// 每成功一次,恢复有效权重1,不超过配置的起始权重
public void onInvokeSuccess(){
if(effectiveWeight < weight) effectiveWeight++;
}
// 每失败一次,有效权重减少1,无底线的减少
public void onInvokeFault(){
effectiveWeight--;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Node node) {
return currentWeight > node.currentWeight ? 1 : (currentWeight.equals(node.currentWeight) ? 0 : -1);
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Node{" +
"ip='" + ip + '\'' +
", port=" + port +
", weight=" + weight +
", effectiveWeight=" + effectiveWeight +
", currentWeight=" + currentWeight +
'}';
}
}一般都是放在配置文件中配置,然后读取指定key的配置文件信息来完成配置。模拟为了简单就直接写代码里了。
package com.yty.proxy;
import com.yty.proxy.lba.Node;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class ProxyConfig {
private static List<Node> nodes = new ArrayList<>();
// 在配置文件中读取:节点集合信息。如果在同一台服务器测试,那就将ip配成一样
static {
nodes.add(new Node("192.168.233.100",8001,2));
nodes.add(new Node("127.0.0.1",8002,5));
nodes.add(new Node("127.0.0.1",8003,3));
}
public static List<Node> getProxyConfig(){
return nodes;
}
}package com.yty.proxy.lba;
public interface Robin {
Node selectNode();
}详细介绍可以阅读前两篇负载均衡算法的文章
package com.yty.proxy.lba;
import com.yty.proxy.ProxyConfig;
import java.util.List;
/**
* 加权轮询算法:平滑加权轮询算法
*/
public class WeightedRoundRobin implements Robin {
private static List<Node> nodes;
// 读取配置信息
static {
nodes = ProxyConfig.getProxyConfig();
}
/**
* 按照当前权重(currentWeight)最大值获取IP
* @return Node
*/
public Node selectNode(){
if (nodes ==null || nodes.size()<=0) return null;
if (nodes.size() == 1) return nodes.get(0);
// 权重之和
Integer totalWeight = 0;
for(Node node : nodes){
totalWeight += node.getEffectiveWeight();
}
synchronized (nodes){
// 选出当前权重最大的节点
Node nodeOfMaxWeight = null;
for (Node node : nodes) {
if (nodeOfMaxWeight == null)
nodeOfMaxWeight = node;
else
nodeOfMaxWeight = nodeOfMaxWeight.compareTo(node) > 0 ? nodeOfMaxWeight : node;
}
// 平滑负载均衡
nodeOfMaxWeight.setCurrentWeight(nodeOfMaxWeight.getCurrentWeight() - totalWeight);
nodes.forEach(node -> node.setCurrentWeight(node.getCurrentWeight()+node.getEffectiveWeight()));
return nodeOfMaxWeight;
}
}
}用于处理代理服务请求的线程类,不同请求创建不同线程来处理
package com.yty.proxy;
import java.io.*;
import java.net.Socket;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class ProxyServerThread implements Runnable {
private Socket proxySocket;
private OutputStream proxyOut;
private InputStream proxyIn;
private Socket socket;
private OutputStream serverOut;
private InputStream serverIn;
public ProxyServerThread(Socket proxySocket) throws IOException {
this.proxySocket = proxySocket;
this.proxySocket.setSoTimeout(6000);
this.proxyOut = proxySocket.getOutputStream();
this.proxyIn = proxySocket.getInputStream();
}
@Override
public void run() {
try {
this.proxyService();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
this.close();
}
}
private void proxyService() throws IOException {
// 代理接收客户端请求
byte[] proxyDataBytes =null;
proxyDataBytes = getData(proxyIn);
System.out.println("代理收到请求数据:"+new String(proxyDataBytes));
if (proxyDataBytes == null){
proxyOut.write("请求内容异常".getBytes());
}
byte[] serverData = this.dispatcherService(proxyDataBytes);
// 代理响应客户端
assert serverData != null;
proxyOut.write(serverData);
proxySocket.shutdownOutput();
System.out.println("代理响应客户端数据:"+new String(proxyDataBytes));
}
private byte[] dispatcherService(byte[] proxyDataBytes){
// 选择节点:发送请求和接收响应信息
Robin wrr = new WeightedRoundRobin();
Node node = wrr.selectNode();
byte[] serverData = null;
try {
this.socket = new Socket(node.getIp(), node.getPort());
socket.setSoTimeout(6000);
serverIn = socket.getInputStream();
serverOut= socket.getOutputStream();
serverOut.write(proxyDataBytes);
socket.shutdownOutput();
serverData = getData(serverIn);
System.out.println("真实服务端响应数据:"+ new String(serverData));
node.onInvokeSuccess();//提权
} catch (IOException e) {
node.onInvokeFault();//降权
serverData = "代理的下游服务器异常".getBytes();
}
System.out.println("负载均衡到:" + node);
return serverData;
}
private byte[] getData(InputStream in) throws IOException {
List<Byte> byteList = new ArrayList<>();
int temp = -1;
while (true) {
temp = in.read();
if (temp != -1)
byteList.add((byte) temp);
else
break;
}
byte[] bytes = new byte[byteList.size()];
for (int i=0;i<byteList.size();i++){
bytes[i]=byteList.get(i);
}
return bytes;
}
private void close() {
try {
if (proxySocket!=null){
proxySocket.shutdownInput();
proxySocket.close();
}
if (socket!=null){
socket.shutdownInput();
socket.close();
}
}catch (IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("代理服务关闭socket资源异常");
}
}
}通过线程池来管理代理服务线程,不同的请求分发到不同线程处理。这里用的是newCachedThreadPool 线程池。
代理服务器在本地启动。这里也可以新建一个类来启动服务,这样可以启动多个代理服务,这里为了简单就直接在本类的main方法启动。可以对比后面的业务服务类,业务服务类就是这么起的,因为要放到不同的服务器启动业务服务。
package com.yty.proxy;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.ServerSocket;
import java.net.Socket;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
public class ProxyServer {
private final Integer port;
private ServerSocket serverSocket;
public ProxyServer(Integer port) {
this.port = port;
}
public void start(){
ExecutorService threadPool = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
try {
serverSocket = new ServerSocket(port);
while (true){
Socket socket = serverSocket.accept();
threadPool.execute(new ProxyServerThread(socket));
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Integer proxyPort=8000;
ProxyServer proxyServer = new ProxyServer(proxyPort);
System.out.println("开启代理服务……");
proxyServer.start();
}
}package com.yty.proxy.server;
public class MyUser {
private String name;
private int age;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public MyUser(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public MyUser() {
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "{" +"name='" + name + '\'' + ", age=" + age + '}';
}
}处理具体业务的类,通过用户名称简单获取信息
package com.yty.proxy.server;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class MyUserService {
private static List<MyUser> list = new ArrayList<>();
static{
list.add(new MyUser("张三",18));
list.add(new MyUser("张三丰",38));
list.add(new MyUser("小白",18));
}
public MyUser findByUsername(String username){
for (MyUser user:list){
if (user.getName().equals(username)){
return user;
}
}
return null;
}
}用于处理业务服务请求的线程类,不同请求创建不同线程来处理
package com.yty.proxy.server;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.net.Socket;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class SocketServerThread implements Runnable {
private Socket socket;
private OutputStream serverOut;
private InputStream serverIn;
public SocketServerThread(Socket socket) throws IOException {
this.socket = socket;
socket.setSoTimeout(6000);
this.serverOut = socket.getOutputStream();
this.serverIn = socket.getInputStream();
}
@Override
public void run() {
try {
this.service();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
this.close();
}
}
private void service() throws IOException {
// 接收客户端请求
byte[] dataBytes =null;
dataBytes = getData(serverIn);
if (dataBytes == null){
serverOut.write("请求内容异常".getBytes());
}
String username = new String(dataBytes);
System.out.println("收到请求数据:"+username);
// 具体业务代码
MyUserService myUserService = new MyUserService();
MyUser user = myUserService.findByUsername(new String(dataBytes));
String serverData = "没有查询到用户" + username + "的数据";
if(user!=null){
serverData = user.toString();
serverOut.write(user.toString().getBytes());
}
System.out.println("响应客户端数据:" + serverData);
}
private byte[] getData(InputStream in) throws IOException {
List<Byte> byteList = new ArrayList<>();
int temp = -1;
while (true) {
temp = in.read();
if (temp != -1)
byteList.add((byte) temp);
else
break;
}
byte[] bytes = new byte[byteList.size()];
for (int i=0;i<byteList.size();i++){
bytes[i]=byteList.get(i);
}
return bytes;
}
private void close() {
try {
if (socket!=null){
socket.shutdownInput();
socket.shutdownOutput();
socket.close();
}
}catch (IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("服务关闭socket资源异常");
}
}
}通过线程池来管理业务服务线程,不同的请求分发到不同线程处理。这里用的也是newCachedThreadPool 线程池。
package com.yty.proxy.server;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.ServerSocket;
import java.net.Socket;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
public class SocketServer {
private final Integer port;
private ServerSocket serverSocket;
private Integer threads = 3;
public SocketServer(Integer port) {
this.port = port;
}
public void start(){
ExecutorService threadPool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(threads);
try {
serverSocket = new ServerSocket(port);
while (true){
Socket socket = serverSocket.accept();
threadPool.execute(new SocketServerThread(socket));
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}本次测试是分在两台服务器测试,1台【192.168.233.100】、另外都是本地【127.0.0.1】。如果觉得麻烦,那就都配成本地【127.0.0.1】,然后起服务都在本地起。
服务1:在IP为192.168.233.100 的服务器启动
package com.yty.proxy.test;
import com.yty.proxy.server.SocketServer;
public class StartServer1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("开启后端服务8001……");
new SocketServer(8001).start();
}
}服务2:在本地服务器启动
package com.yty.proxy.test;
import com.yty.proxy.server.SocketServer;
public class StartServer2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("开启后端服务8002……");
new SocketServer(8002).start();
}
}服务3:在本地服务器启动
package com.yty.proxy.test;
import com.yty.proxy.server.SocketServer;
public class StartServer3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("开启后端服务8003……");
new SocketServer(8003).start();
}
}package com.yty.proxy.test;
import java.io.BufferedInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.net.Socket;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
String ip = "127.0.0.1";
int port = 8000;
Socket socket = new Socket(ip, port);
socket.setSoTimeout(6000);
OutputStream out = socket.getOutputStream();
InputStream in = socket.getInputStream();
// 发送数据
out.write("小白".getBytes());
out.flush();
socket.shutdownOutput();
// 读取数据
byte[] data = new Client().getData(in);
System.out.println("响应数据:"+new String(data));
out.close();
}
private byte[] getData(InputStream in) throws IOException {
BufferedInputStream bin = new BufferedInputStream(in);
List<Byte> byteList = new ArrayList<>();
while (true) {
int temp = bin.read();
if (temp != -1)
byteList.add((byte) temp);
else
break;
}
byte[] bytes = new byte[byteList.size()];
for (int i=0;i<byteList.size();i++){
bytes[i]=byteList.get(i);
}
return bytes;
}
}在代理配置类(ProxyConfig)中指定的服务器启动三个业务服务;
在你喜欢的服务器中启动代理服务(ProxyServer),这里在本地启动【127.0.0.1】;
客户端在本地测试咯(IP必须是代理服务器的IP,这里测试的代理服务器IP是【127.0.0.1】。
所有服务启动后的截图:
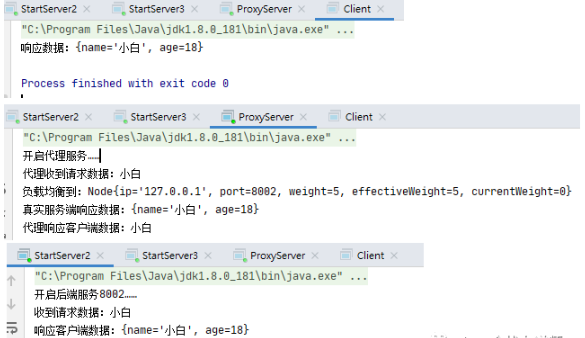
正常命中权重最高的节点2服务:节点信息在代理服务器中打印出来了【127.0.0.1、8002】。这些日志信息正常情况是写入到日志文件,这里只在控制台打印出来。
改了用户名再请求试试,发现忘记打印请求数据了……
第二次命中节点3服务,跟平滑加权算法预定的结果一样。
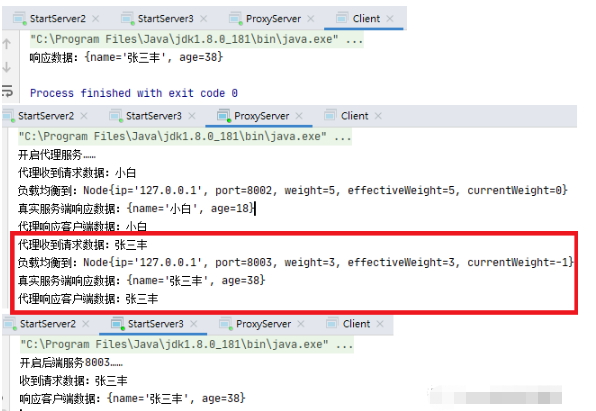
这次命中了节点2:192.168.233.100,8001的服务。到此可以看到平滑加权轮询算法正常运作中。
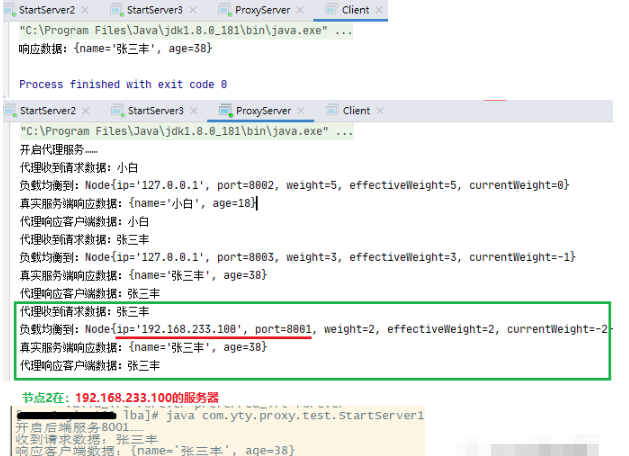
通过平滑加权轮询算法运算,我们知道这次肯定命中节点2服务。所以,在发起请求前,先关闭节点2服务,再由客户端发起请求。
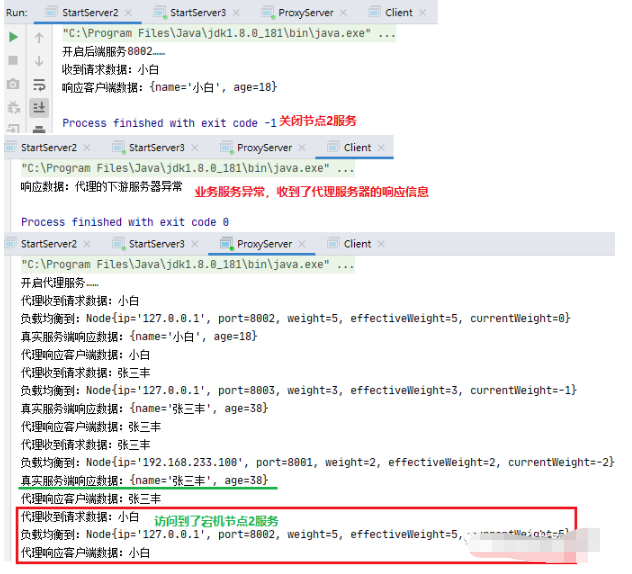
细心的应该发现,有效权重没变小啊,是不是降权有问题?
其实不是,是打印信息的位置没放对……。要在下次访问才可以看到上一次的降权结果,额,有点呆(上面的代码我已经改了)。

先把宕机的服务启动起来,然后多测试几次,看看测试结果。可以看到,权重降低后又提起来了,说明测试提权成功。

还有两个点没测:第一个是一直降权后,会不会出现宕机的服务不再分配到?这就起到”剔除“宕机服务的效果?第二个是服务恢复后,会不会出现宕机再起的服务需要慢慢恢复权重,直到一定值后才可以分配到?





