集合是一种长度可变,存储数据的数据结构多样,存储对象多样的一种数据容器。Java中集合可分为:List集合、Set集合、HashMap集合,等。
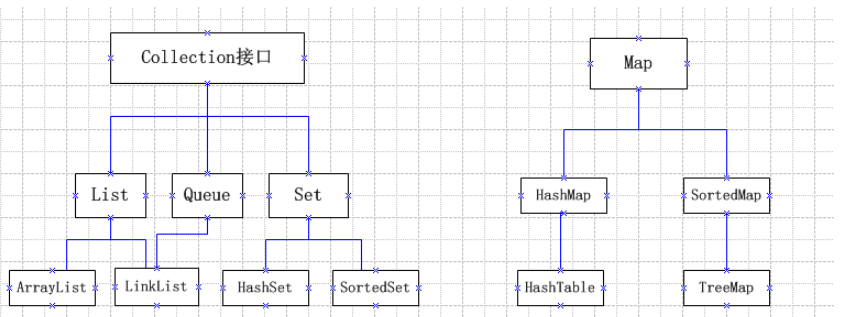
collection是Java中所有值存储集合的顶级接口,因此它的所有直接或者间接实现类都有它的非私有方法,我们可以从它的方法开始了解这个体系的功能实现。
boolean add(E e) 确保此 collection 包含指定的元素。 boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) 将指定 collection 中的所有元素都添加到此 collection 中。 void clear() 移除此 collection 中的所有元素。 boolean contains(Object o) 如果此 collection 包含指定的元素,则返回 true。 boolean containsAll(Collection<?> c) 如果此 collection 包含指定 collection 中的所有元素,则返回 true。 boolean equals(Object o) 比较此 collection 与指定对象是否相等。 int hashCode() 返回此 collection 的哈希码值。 boolean isEmpty() 如果此 collection 不包含元素,则返回 true。 Iterator<E> iterator() 返回在此 collection 的元素上进行迭代的迭代器。 boolean remove(Object o) 从此 collection 中移除指定元素的单个实例,如果存在的话)。 boolean removeAll(Collection<?> c) 移除此 collection 中那些也包含在指定 collection 中的所有元素。 boolean retainAll(Collection<?> c) 仅保留此 collection 中那些也包含在指定 collection 的元素。 int size() 返回此 collection 中的元素数。 Object[] toArray() 返回包含此 collection 中所有元素的数组。 <T> T[] toArray(T[] a) 返回包含此 collection 中所有元素的数组;返回数组的运行时类型与指定数组的运行时类型相同。
List,是单列集合,存储的是一组插入有序的数据,并且数据可以重复。
List集合
LinkedList
ArrayList
示例:
public class CollectionTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List list = new ArrayList();
//添加元素,boolean add(E e) 确保此 collection 包含指定的元素
list.add("张三");
list.add(1);
list.add('A');
System.out.println(list);//[张三, 1, A]
//boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c)
// 将指定 collection 中的所有元素都添加到此 collection 中
List list1 = new ArrayList();
list.add("java");
list.add("MySQL");
list.addAll(list1);
System.out.println(list);//[张三, 1, A, java, MySQL]
//boolean contains(Object o)
// 如果此 collection 包含指定的元素,则返回 true。
System.out.println(list.contains("java"));//true
//boolean remove(Object o)
// 从此 collection 中移除指定元素的单个实例,如果存在的话)。
System.out.println(list.remove("java"));//true
// int size()
// 返回此 collection 中的元素数。
System.out.println(list.size());//4
//set(int index, E element)
// 用指定的元素替代此列表中指定位置上的元素。
//并返回被修改的值
System.out.println(list.set(1, "李四"));
//get(int index)
// 返回此列表中指定位置上的元素。
System.out.println(list.get(1));
// Iterator<E> iterator()
// 返回在此 collection 的元素上进行迭代的迭代器。
//集合的遍历
Iterator iterator = list.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()){
System.out.println(iterator.next());
}
}说明:ArrayList底层是使用数组的形式创建集合的,因此基于数组的特性,此集合对数据的查找很快速,但是在删除或移动大量数据操作上会显得缓慢。它适合用于快速查找,但不适合做删除多的操作。
LinkedList:双向链表,内部没有声明数组,而是定义了Node类型的first 和last,用于记录首末元素。同时,定义内部类Node,作为LinkedList中 保存数据的基本结构。Node除了保存数据,还定义了两个变量:
prev变量记录前一个元素的位置
next变量记录下一个元素的位置
特点:
数据有序
底层结构为链表
ArrayList比较:
LinkedList的添加元素速度比ArrayList快;
LinkedList的查询速度比ArrayList慢;
底层数据结构不同:LinkedList用的是链表结构,而ArrayList底层使用 的是数组结构;
说明:LinkedList一般用于添加频繁的操作,ArrayList一般用于频繁查询 的操作。
示例:
public class Stack {
private LinkedList data = null;
public Stack(){
data = new LinkedList();
}
// 添加元素
public boolean push(Object element) {
data.addFirst(element);
return true;
}
// 获取元素
public Object pop() {
return data.pollFirst();
}
// 判断集合是否为空
public boolean isEmpty() {
return data.isEmpty();
}
// 迭代元素
public void list() {
Iterator it = data.iterator();
while(it.hasNext()){
System.out.println(it.next());
}
}
}
public class MyStack {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stack stack = new Stack();
stack.push("张三");
stack.push("李四");
stack.push("王五");
stack.list();
System.out.println("-------------");
Object pop = stack.pop();
System.out.println(pop);
}
}HashSet 是 Set 接口的典型实现,大多数时候使用 Set 集合时都使用 这个实现类。
HashSet 按 Hash 算法来存储集合中的元素,因此具有很好的存取、 查找、删除性能。
HashSet 具有以下特点:不能保证元素的排列顺序
HashSet 不是线程安全的
集合元素可以是 null
不能添加重复元素
HashSet 集合判断两个元素相等的标准:两个对象通过 hashCode() 方法比较相等,并且两个对象的 equals() 方法返回值也相等。
对于存放在Set容器中的对象,对应的类一定要重写equals()和 hashCode(Object obj)方法,以实现对象相等规则。即:“相等的对象必须具有相等的散列码”。
示例:
public static void main(String[] args) {
Set set = new HashSet();
// 添加
// boolean add(E e) :把指定的元素添加到集合中
set.add("hello");
set.add("world");
set.add("world");
set.add(null);
System.out.println(set);
// 注:Set集合中元素是无序,并且不能重复
// boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) :把指定的集合添加到集合中
Set set1 = new HashSet();
set1.add("aaa");
set1.add("linux");
;
set.addAll(set1);
System.out.println(set);
// boolean remove(Object o) :从集合中删除指定元素
set.remove("hello");
System.out.println(set);
// boolean removeAll(Collection<?> c) :从集合中删除指定集合中的所有元素
set1.add("aaa");
set1.add("linux");
set.removeAll(set1);
System.out.println(set);
// void clear() :清空集合中所有元素
set.clear();
System.out.println(set);
// int size() :获取集合的元素个数
int size = set.size();
System.out.println(size);
// boolean contains(Object o) :判断集合中是否包含指定元素,包含为true,否则为false;
System.out.println(set.contains("aaa"));
// boolean isEmpty() :判断集合是否为空
System.out.println(set.isEmpty());
}说明:在HashSet添加元素时,会首先比较两个元素的hashCode值是不相等,如 果不相等则直接添加;如果相等再判断两个元素的equals的值是否相等, 如果相等则不添加,如果不相等则添加。
TreeSet和TreeMap采用红黑树的存储结构
特点:有序,查询速度比List快
使用TreeSet集合是,对象必须具有可比较性。而要让对象具有可比较性有 两种方式:
第一种:实现Comparable接口,并重写compareTo()方法:
第二种:写一个比较器类,让该类去实现Comparator接口,并重写 comare()方法。
示例:
public class Student implements Comparable<Student>{
private String name;
private int age;
private String sex;
private int height;
public Student() {
}
public Student(String name, int age, String sex, int height) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.sex = sex;
this.height = height;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getSex() {
return sex;
}
public void setSex(String sex) {
this.sex = sex;
}
public int getHeight() {
return height;
}
public void setHeight(int height) {
this.height = height;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) return true;
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;
Student student = (Student) o;
return age == student.age &&
height == student.height &&
Objects.equals(name, student.name) &&
Objects.equals(sex, student.sex);
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return Objects.hash(name, age, sex, height);
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
", sex='" + sex + '\'' +
", height=" + height +
'}';
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Student stu) {
if (stu.getAge() > this.getAge()){
return 1;
}
if (stu.getAge() < this.getAge()){
return -1;
}
return stu.getName().compareTo(this.getName());
}
}public class TreeSetTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
TreeSet treeSet = new TreeSet();
Student student1 = new Student("张三", 20, "男", 165);
Student student2 = new Student("李四", 21, "男", 170);
Student student3 = new Student("王五", 19, "女", 160);
Student student4 = new Student("赵六", 18, "女", 165);
Student student5 = new Student("田七", 20, "男", 175);
treeSet.add(student1);
treeSet.add(student2);
treeSet.add(student3);
treeSet.add(student4);
treeSet.add(student5);
System.out.println(treeSet);
}
}public class Teacher {
private String name;
public Teacher(){}
public Teacher(String name){
this.name = name;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Teacher{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
'}';
}
}public class TreeSetTest2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Teacher teacher1 = new Teacher("11");
Teacher teacher2 = new Teacher("12");
Teacher teacher3 = new Teacher("13");
Teacher teacher4 = new Teacher("14");
Teacher teacher5 = new Teacher("15");
TreeSet treeSet1 = new TreeSet(new Comparator() {
@Override
public int compare(Object o1, Object o2) {
return o1.hashCode() - o2.hashCode();
}
});
treeSet1.add(teacher1);
treeSet1.add(teacher2);
treeSet1.add(teacher3);
treeSet1.add(teacher4);
treeSet1.add(teacher5);
System.out.println(treeSet1);
}
}说明:HashSet去重是依靠hashCode和equals()方法,而TreeSet去重则 依靠的是比较器。





