删除链表中等于给定值val的所有节点。【OJ链接】
定义两个指针prev、cur,cur指向头节点的下一个节点,prev始终指向cur的前一个结点(方便删除节点)。通过cur指针去遍历链表,和val值比较,相同就删除这个节点。最后再来比较头节点。
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode removeElements(ListNode head, int val) {
if(head==null){
return null;
}
ListNode prev=head;
ListNode cur=head.next;
while(cur!=null){
if(cur.val==val){
prev.next=cur.next;
cur=cur.next;
}else{
prev=cur;
cur=cur.next;
}
}
if(head.val==val){
head=head.next;
}
return head;
}
}反转一个链表。【OJ链接】

在遍历链表时,将当前节点的 指针改为指向前一个节点。由于节点没有引用其前一个节点,因此必须事先存储其前一个节点。在更改引用之前,还需要存储后一个节点。最后返回新的头引用。
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
if(head==null){
return null;
}
ListNode cur=head.next;
head.next=null;
while(cur!=null){
ListNode curNext=cur.next;
cur.next=head;
head=cur;
cur=curNext;
}
return head;
}
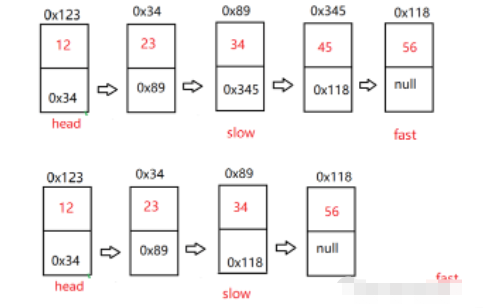
}给定一个带有头节点的非空单链表,返回链表的中间节点。如果有两个中间节点,则返回第二个中间节点。【OJ链接】
我们可以定义两个快慢指针(fast、slow),都指向头节点。快指针每次走两步,慢指针每次走一步。链表有偶数个节点时,fast=null时slow为中间节点;链表有奇数个节点时,fast.next=null时slow为中间节点。
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode middleNode(ListNode head) {
if(head==null){
return null;
}
ListNode slow=head;
ListNode fast=head;
while(fast!=null&&fast.next!=null){
fast=fast.next.next;
slow=slow.next;
}
return slow;
}
}输入一个链表,返回该链表中倒数第K个节点。【OJ链接】
这个题和找中间节点的思路相似。定义两个指针(fast、slow)。在K合理的前提下,我们可以让快指针先走K-1步,然后快慢指针同时向后走,当fast到达链表结尾时,slow就指向倒数第K个节点。
/*
public class ListNode {
int val;
ListNode next = null;
ListNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode FindKthToTail(ListNode head,int k) {
if(k<=0||head==null){
return null;
}
ListNode fast=head;
ListNode slow=head;
while(k-1>0){
if(fast.next==null){
return null;
}
fast=fast.next;
//先让快节点走k-1步
k--;
}
while(fast.next!=null){
fast=fast.next;
slow=slow.next;
}
return slow;
}
}将两个有序链表合并为一个有序链表并返回。新链表是通过拼接给定的两个链表的所有节点组成的。【OJ链接】
解这个题,需要定义虚假节点来充当新链表的头节点。通过两个链表的头节点去遍历两个节点,去比较两个链表对应节点的值,将值小的节点连接到新链表的后面,知道两个链表遍历完,当其中一个链表为空时,直接将另一个链表连接到新链表后面即可。
class Solution {
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode list1, ListNode list2) {
if(list1==null){
return list2;
}
if(list2==null){
return list1;
}
//创建虚拟节点,充当新链表的头节点,值不代表任何意义
ListNode node=new ListNode(-1);
ListNode cur=node;
while(list1!=null&&list2!=null){
if(list1.val<list2.val){
cur.next=list1;
list1=list1.next;
}else{
cur.next=list2;
list2=list2.next;
}
cur=cur.next;
}
if(list1==null){
cur.next=list2;
}else{
cur.next=list1;
}
return node.next;
}
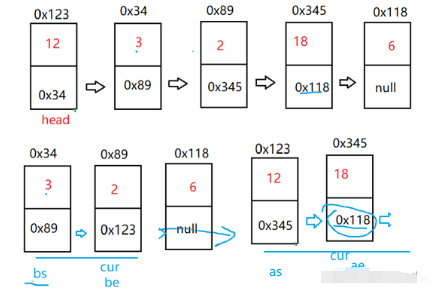
}将一个链表按照给定值X划分为两部分,所有小于X的节点排在大于或等于X的节点之前。不改变节点原来的顺序。【OJ链接】
首先我们需要定义四个指针(bs、be、as、ae)分别表示小于X部分链表的头节点和尾节点、大于X部分链表的头节点和尾节点。通过头节点遍历链表,将链表分为两部分。最后将两个链表连接起来即可。需要特别注意,当小于X部分链表不为空时,我们需要手动将ae.next置为空。
/*
public class ListNode {
int val;
ListNode next = null;
ListNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}*/
public class Partition {
public ListNode partition(ListNode pHead, int x) {
if(pHead==null){
return null;
}
ListNode bs=null;
ListNode be=null;
ListNode as=null;
ListNode ae=null;
ListNode cur=pHead;
while(cur!=null){
if(cur.val<x){
if(bs==null){
bs=cur;
be=cur;
}else{
be.next=cur;
be=cur;
}
}else{
if(as==null){
as=cur;
ae=cur;
}else{
ae.next=cur;
ae=cur;
}
}
cur=cur.next;
}
if(bs==null){
return as;
//如果小于X部分为空,则直接返回大于X部分即可。此时ae.next一定为null
}
be.next=as;//否则连接小于X和大于X部分
if(as!=null){
ae.next=null;
//当小于X部分不为空时,ae.next可能不为null,需要手动置为null
}
return bs;
}
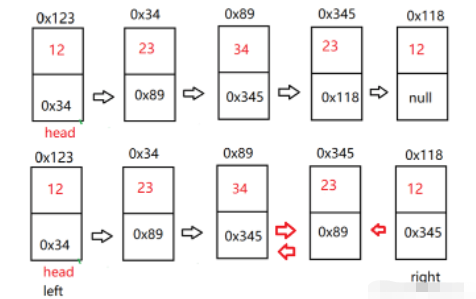
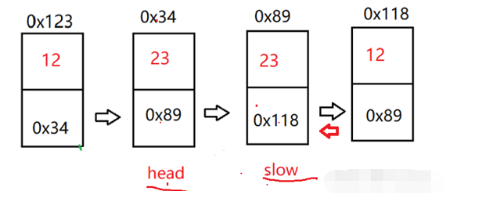
}判断链表是不是回文链表。【OJ链接】
首先我们需要找到链表的中间节点,然后将后半段链表反转。最后通过两边来逐步比较即可。特别注意,当链表结点个数为偶数时,因为中间节点的缘故,两边遍历时,无法相遇,需要特殊处理。
/*
public class ListNode {
int val;
ListNode next = null;
ListNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}*/
public class PalindromeList {
public boolean chkPalindrome(ListNode A) {
if(A==null){
return false;
}
if(A.next==null){
return true;
}
//求链表的中间节点
ListNode slow=A;
ListNode fast=A;
while(fast!=null&&fast.next!=null){
fast=fast.next.next;
slow=slow.next;
}
//反转后半段链表
ListNode cur=slow.next;
while(cur!=null){
ListNode curNext=cur.next;
cur.next=slow;
slow=cur;
cur=curNext;
}
//判断回文链表
while(slow!=A){
if(slow.val!=A.val){
return false;
}
if(A.next==slow){
return true;
}
slow=slow.next;
A=A.next;
}
return true;
}
}输入两个链表,输出两个链表的第一个公共节点。没有返回NULL。【OJ链接】
两个链表相交呈现Y字型。那么两个链表长度的差肯定是未相交前两个链表节点的差。我们需要求出两个链表的长度。定义两个指针(pl、ps),让pl指向长的链表,ps指向短的链表。求出两个链表的长度差len。让pl想走len步。这样两个链表的剩余长度就相同。此时两个指针同时遍历连个链表,如果其指向一致,则两个链表相交,否则,两个链表不相交。
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) {
* val = x;
* next = null;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
//求链表长度
public int len(ListNode head){
int len=0;
while(head!=null){
head=head.next;
len++;
}
return len;
}
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
if(headA==null||headB==null){
return null;
}
ListNode pl=headA;
ListNode ps=headB;
int lenA=len(headA);
int lenB=len(headB);
int len=lenA-lenB;
if(len<0){
//pl指向长的链表,ps指向短的链表
pl=headB;
ps=headA;
len=-len;
}
while(len--!=0){
pl=pl.next;
}
while(pl!=null){
if(pl==ps){
return pl;
}
pl=pl.next;
ps=ps.next;
}
return null;
}
}判断链表中是否有环。【OJ链接】
还是快慢指针。慢指针一次走一步,快指针一次走两步。两个指针从链表起始位置开始运行。如果链表带环则一定会在环中相遇,否则快指针率先走到链表的末尾。
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) {
* val = x;
* next = null;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public boolean hasCycle(ListNode head) {
if(head==null||head.next==null){
return false;//链表为空或者只有一个节点时,没有环
}
ListNode slow=head;
ListNode fast=head;
while(fast!=null&&fast.next!=null){
fast=fast.next.next;
slow=slow.next;
if(fast==slow){
return true;
//如果快慢节点可以相遇,表示链表有环
}
}
return false;
}
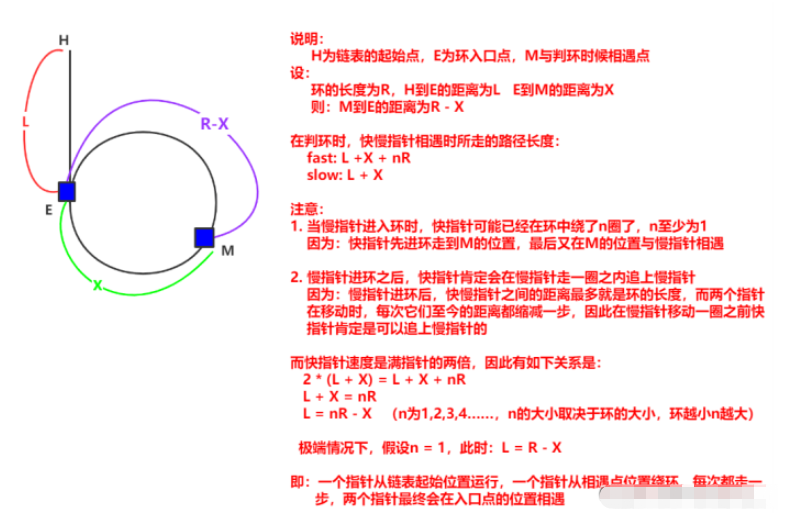
}给定一个链表,判断链表是否有环并返回入环的节点。如果没有环,返回NULL。【OJ链接】
让一个指针从链表的其实在位置开始遍历,同时另一个指针从上题中两只真相与的位置开始走,两个指针再次相遇时的位置肯定为环的入口
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) {
* val = x;
* next = null;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
//判断链表是否有环,并返回第一次快慢节点相交的位置
public ListNode hasCycle(ListNode head){
if(head==null||head.next==null){
return null;
}
ListNode slow=head;
ListNode fast=head;
while(fast!=null&&fast.next!=null){
slow=slow.next;
fast=fast.next.next;
if(slow==fast){
return slow;
}
}
return null;
}
//当返回的结点与头节点再次相交时,为环的入口
public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) {
ListNode node=hasCycle(head);
if(node==null){
return null;
}else{
while(head!=node){
head=head.next;
node=node.next;
}
}
return head;
}
}





