a 创建双向链表:
在创建哈夫曼树的过程中,需要不断对结点进行更改和删除,所以选用双向链表的结构更容易
'''C
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <windows.h>
//哈夫曼树结构体,数据域存储字符及其权重
typedef struct node
{
char c;
int weight;
struct node *lchild, *rchild;
}Huffman, *Tree;
//双向链表结构体,数据域存储哈夫曼树结点
typedef struct list
{
Tree root;
struct list *pre;
struct list *next;
}List, *pList;
//创建双向链表,返回头结点指针
pList creatList()
{
pList head = (pList)malloc(sizeof(List));
pList temp1 = head;
pList temp2 = (pList)malloc(sizeof(List));
temp1->pre = NULL;
temp1->next = temp2;
temp1->root = (Tree)malloc(sizeof(Huffman));
temp1->root->c = 'a';
temp1->root->weight = 22;
temp1->root->lchild = NULL;
temp1->root->rchild = NULL;
temp2->pre = temp1;
temp1 = temp2;
temp2 = (pList)malloc(sizeof(List));
temp1->next = temp2;
temp1->root = (Tree)malloc(sizeof(Huffman));
temp1->root->c = 'b';
temp1->root->weight = 5;
temp1->root->lchild = NULL;
temp1->root->rchild = NULL;
temp2->pre = temp1;
temp1 = temp2;
temp2 = (pList)malloc(sizeof(List));
temp1->next = temp2;
temp1->root = (Tree)malloc(sizeof(Huffman));
temp1->root->c = 'c';
temp1->root->weight = 38;
temp1->root->lchild = NULL;
temp1->root->rchild = NULL;
temp2->pre = temp1;
temp1 = temp2;
temp2 = (pList)malloc(sizeof(List));
temp1->next = temp2;
temp1->root = (Tree)malloc(sizeof(Huffman));
temp1->root->c = 'd';
temp1->root->weight = 9;
temp1->root->lchild = NULL;
temp1->root->rchild = NULL;
temp2->pre = temp1;
temp1 = temp2;
temp2 = (pList)malloc(sizeof(List));
temp1->next = temp2;
temp1->root = (Tree)malloc(sizeof(Huffman));
temp1->root->c = 'e';
temp1->root->weight = 44;
temp1->root->lchild = NULL;
temp1->root->rchild = NULL;
temp2->pre = temp1;
temp1 = temp2;
temp2 = (pList)malloc(sizeof(List));
temp1->next = temp2;
temp1->root = (Tree)malloc(sizeof(Huffman));
temp1->root->c = 'f';
temp1->root->weight = 12;
temp1->root->lchild = NULL;
temp1->root->rchild = NULL;
temp2->pre = temp1;
temp1 = temp2;
temp1->next = NULL;
temp1->root = (Tree)malloc(sizeof(Huffman));
temp1->root->c = 'g';
temp1->root->weight = 65;
temp1->root->lchild = NULL;
temp1->root->rchild = NULL;
return head;
}b创建栈结构:
解码过程需要用到两个栈,一个用来存放树结点,一个用来存放码0和1
'''C
#define STACK_INIT_SIZE 100 //栈初始开辟空间大小
#define STACK_INCREMENT 10 //栈追加空间大小
//字符栈结构体,存放编码'0'和'1'
typedef struct {
char *base;
char *top;
int size;
}charStack;
//栈初始化
charStack charStackInit()
{
charStack s;
s.base = (char *)malloc(sizeof(char)*STACK_INIT_SIZE);
s.top = s.base;
s.size = STACK_INIT_SIZE;
return s;
}
//入栈
void charPush(charStack *s, char e)
{
if(s->top - s->base >= s->size)
{
s->size += STACK_INCREMENT;
s->base = realloc(s->base, sizeof(char)*s->size);
}
*s->top = e;
s->top++;
}
//出栈
char charPop(charStack *s)
{
if(s->top != s->base)
{
s->top--;
return *s->top;
}
return -1;
}
//得到栈顶元素,但不出栈
char charGetTop(charStack *s)
{
s->top--;
char temp = *s->top;
s->top++;
return temp;
}
//栈结构体,存放哈夫曼树结点
typedef struct
{
Huffman *base;
Huffman *top;
int size;
}BiStack;
//栈初始化
BiStack stackInit()
{
BiStack s;
s.base = (Huffman *)malloc(sizeof(Huffman)*STACK_INIT_SIZE);
s.top = s.base;
s.size =STACK_INIT_SIZE;
return s;
}
//入栈
void push(BiStack *s, Huffman e)
{
if(s->top - s->base >= s->size)
{
s->size += STACK_INCREMENT;
s->base = (Huffman *)realloc(s->base, sizeof(Huffman)*s->size);
}
*s->top = e;
s->top++;
}
//出栈
Huffman pop(BiStack *s)
{
Huffman temp;
s->top--;
temp = *s->top;
return temp;
}
//得到栈顶元素,但不出栈
Huffman getTop(BiStack s)
{
Huffman temp;
s.top--;
temp = *s.top;
return temp;
}
char stack[7][10]; //记录a~g的编码
//遍历栈,得到字符c的编码
void traverseStack(charStack s, char c)
{
int index = c - 'a';
int i = 0;
while(s.base != s.top)
{
stack[index][i] = *s.base;
i++;
s.base++;
}
}c 创建哈夫曼树:
'''C
//通过双向链表创建哈夫曼树,返回根结点指针
Tree creatHuffman(pList head)
{
pList list1 = NULL;
pList list2 = NULL;
pList index = NULL;
Tree root = NULL;
while(head->next != NULL) //链表只剩一个结点时循环结束,此结点数据域即为哈夫曼树的根结点
{
list1 = head;
list2 = head->next;
index = list2->next;
root = (Tree)malloc(sizeof(Huffman));
while(index != NULL) //找到链表中权重最小的两个结点list1,list2
{
if(list1->root->weight > index->root->weight || list2->root->weight > index->root->weight)
{
if(list1->root->weight > list2->root->weight) list1 = index;
else list2 = index;
}
index = index->next;
}
//list1和list2设为新结点的左右孩子
if(list2->root->weight > list1->root->weight)
{
root->lchild = list1->root;
root->rchild = list2->root;
}
else
{
root->lchild = list2->root;
root->rchild = list1->root;
}
//新结点字符统一设为空格,权重设为list1与list2权重之和
root->c = ' ';
root->weight = list1->root->weight + list2->root->weight;
//list1数据域替换成新结点,并删除list2
list1->root = root;
list2->pre->next = list2->next;
if(list2->next != NULL)
list2->next->pre = list2->pre;
}
return head->root;
}d编码:
'''C
char stack[7][10]; //记录a~g的编码
//遍历栈,得到字符c的编码
void traverseStack(charStack s, char c)
{
int index = c - 'a';
int i = 0;
while(s.base != s.top)
{
stack[index][i] = *s.base;
i++;
s.base++;
}
}
//通过哈夫曼树编码
void encodeHuffman(Tree T)
{
BiStack bs = stackInit();
charStack cs = charStackInit();
Huffman root = *T;
Tree temp = NULL;
push(&bs, root); //根结点入栈
while(bs.top != bs.base) //栈空表示遍历结束
{
root = getTop(bs);
temp = root.lchild; //先访问左孩子
while(temp != NULL) //左孩子不为空
{
//将结点左孩子设为空,代表已访问其左孩子
root.lchild = NULL;
pop(&bs);
push(&bs, root);
//左孩子入栈
root = *temp;
temp = root.lchild;
push(&bs, root);
//'0'入字符栈
charPush(&cs, '0');
}
temp = root.rchild; //后访问右孩子
while(temp == NULL) //右孩子为空,代表左右孩子均已访问,结点可以出栈
{
//结点出栈
root = pop(&bs);
//寻到叶子结点,可以得到结点中字符的编码
if(root.c != ' ')
traverseStack(cs, root.c);
charPop(&cs); //字符栈出栈
if(bs.top == bs.base) break; //根结点出栈,遍历结束
//查看上一级结点是否访问完左右孩子
root = getTop(bs);
temp = root.rchild;
}
if(bs.top != bs.base)
{
//将结点右孩子设为空,代表已访问其右孩子
root.rchild = NULL;
pop(&bs);
push(&bs, root);
//右孩子入栈
root = *temp;
push(&bs, root);
//'1'入字符栈
charPush(&cs, '1');
}
}
}e解码:
'''C
char decode[100]; //记录解码得到的字符串
//通过哈夫曼树解码
void decodeHuffman(Tree T, char *code)
{
int cnt = 0;
Tree root;
while(*code != '\0') //01编码字符串读完,解码结束
{
root = T;
while(root->lchild != NULL) //找到叶子结点
{
if(*code != '\0')
{
if(*code == '0')
root = root->lchild;
else
root = root->rchild;
code++;
}
else break;
}
decode[cnt] = root->c; //叶子结点存放的字符即为解码得到的字符
cnt++;
}
}f主函数:
'''C
void main()
{
pList pl = creatList();
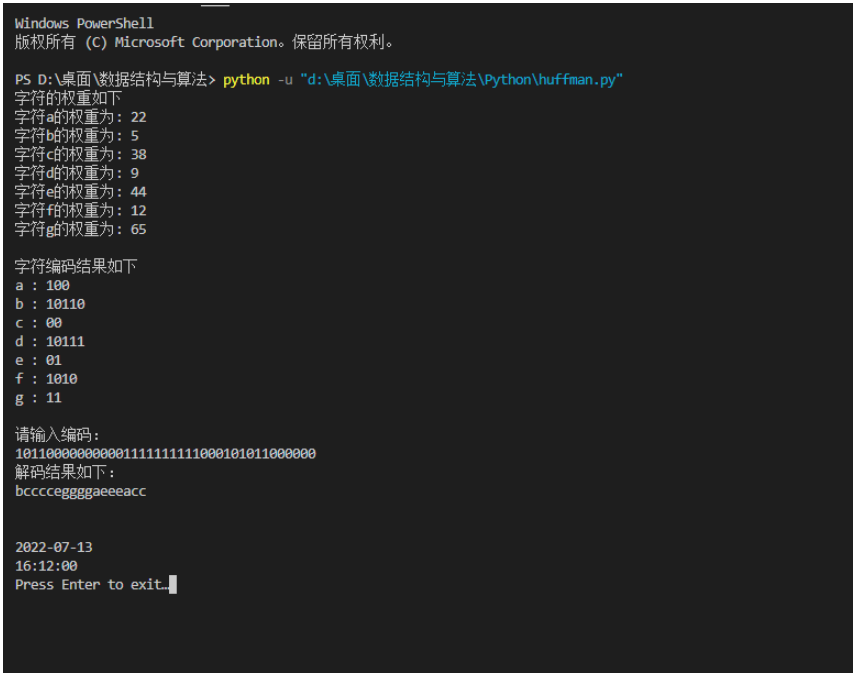
printf("字符的权重如下\n");
for(pList l = pl; l->next != NULL; l = l->next)
printf("字符%c的权重是 %d\n", l->root->c, l->root->weight);
Tree T = creatHuffman(pl);
encodeHuffman(T);
printf("\n\n字符编码结果如下\n");
for(int i = 0; i < 7; i++)
printf("%c : %s\n", i+'a', stack[i]);
char code[100];
printf("\n\n请输入编码:\n");
scanf("%s", code);
printf("解码结果如下:\n");
decodeHuffman(T, code);
printf("%s\n", decode);
printf("\n\n");
system("date /T");
system("TIME /T");
system("pause");
exit(0);
}
a创建哈夫曼树:
#coding=gbk
import datetime
import time
from pip._vendor.distlib.compat import raw_input
#哈夫曼树结点类
class Huffman:
def __init__(self, c, weight):
self.c = c
self.weight = weight
self.lchild = None
self.rchild = None
#创建结点左右孩子
def creat(self, lchild, rchild):
self.lchild = lchild
self.rchild = rchild
#创建列表
def creatList():
list = []
list.append(Huffman('a', 22))
list.append(Huffman('b', 5))
list.append(Huffman('c', 38))
list.append(Huffman('d', 9))
list.append(Huffman('e', 44))
list.append(Huffman('f', 12))
list.append(Huffman('g', 65))
return list
#通过列表创建哈夫曼树,返回树的根结点
def creatHuffman(list):
while len(list) > 1: #列表只剩一个结点时循环结束,此结点即为哈夫曼树的根结点
i = 0
j = 1
k = 2
while k < len(list): #找到列表中权重最小的两个结点list1,list2
if list[i].weight > list[k].weight or list[j].weight > list[k].weight:
if list[i].weight > list[j].weight:
i = k
else:
j = k
k += 1
root = Huffman(' ', list[i].weight + list[j].weight) #新结点字符统一设为空格,权重设为list1与list2权重之和
if list[i].weight < list[j].weight: #list1和list2设为新结点的左右孩子
root.creat(list[i], list[j])
else:
root.creat(list[j], list[i])
#list1数据域替换成新结点,并删除list2
list[i] = root
list.remove(list[j])
return list[0]b编码:
#通过哈夫曼树编码 def encodeHuffman(T): code = [[], [], [], [], [], [], []] #列表实现栈结构 treeStack = [] codeStack = [] treeStack.append(T) while treeStack != []: #栈空代表遍历结束 root = treeStack[-1] temp = root.lchild while temp != None: #将结点左孩子设为空,代表已访问其左孩子 root.lchild = None #左孩子入栈 treeStack.append(temp) root = temp temp = root.lchild #0入编码栈 codeStack.append(0) temp = root.rchild #后访问右孩子 while temp == None: #右孩子为空,代表左右孩子均已访问,结点可以出栈 root = treeStack.pop() #结点出栈 #寻到叶子结点,可以得到结点中字符的编码 if root.c != ' ': codeTemp = codeStack.copy() code[ord(root.c) - 97] = codeTemp if treeStack == []: #根结点出栈,遍历结束 break codeStack.pop() #编码栈出栈 #查看上一级结点是否访问完左右孩子 root = treeStack[-1] temp = root.rchild if treeStack != []: treeStack.append(temp) #右孩子入栈 root.rchild = None #将结点右孩子设为空,代表已访问其右孩子 codeStack.append(1) #1入编码栈 return code
c解码:
#通过哈夫曼树解码 def decodeHuffman(T, strCode): decode = [] index = 0 while index < len(strCode): #01编码字符串读完,解码结束 root = T while root.lchild != None: #找到叶子结点 if index < len(strCode): if strCode[index] == '0': root = root.lchild else: root = root.rchild index += 1 else: break decode.append(root.c) #叶子结点存放的字符即为解码得到的字符 return decode
d主函数:
if __name__ == '__main__':
list = creatList()
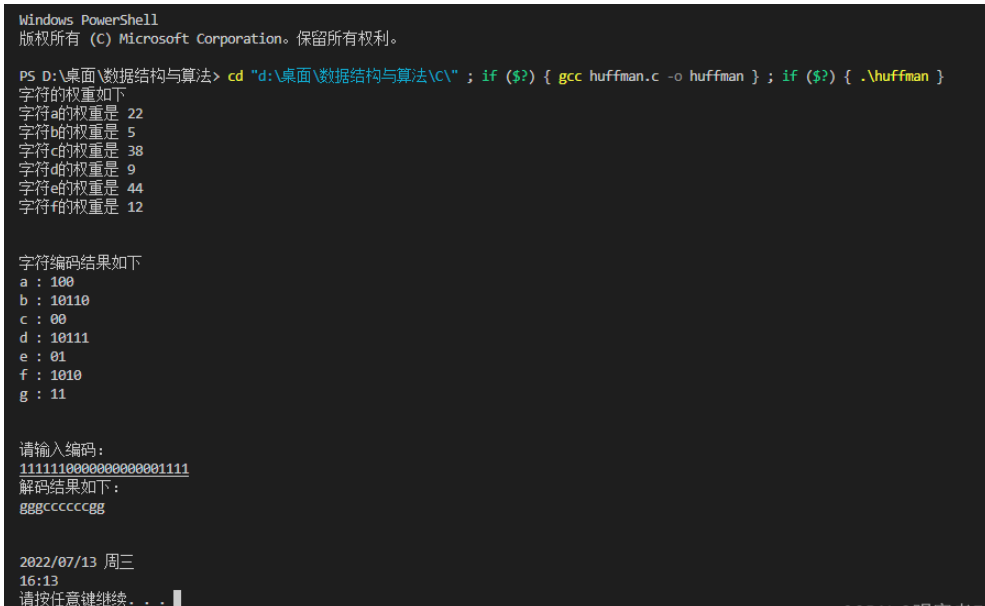
print("字符的权重如下")
for i in range(len(list)):
print("字符{}的权重为: {}".format(chr(i+97), list[i].weight))
T = creatHuffman(list)
code = encodeHuffman(T)
print("\n字符编码结果如下")
for i in range(len(code)):
print(chr(i+97), end=' : ')
for j in range(len(code[i])):
print(code[i][j], end='')
print("")
strCode = input("\n请输入编码:\n")
#哈夫曼树在编码时被破坏,必须重建哈夫曼树
list = creatList()
T = creatHuffman(list)
decode = decodeHuffman(T, strCode)
print("解码结果如下:")
for i in range(len(decode)):
print(decode[i], end='')
print("\n\n")
datetime = datetime.datetime.now()
print(datetime.strftime("%Y-%m-%d\n%H:%M:%S"))
input("Press Enter to exit…")