这个是错误的代码:
class BB
{
static int a = 0 ;
public BB()
{
a++ ;
System.out.println("执行BB" + a) ;
}
public void printA()
{
System.out.println("a= " + a) ;
}
}
public class CC
{
static
{
a = new BB() ;
a.printA() ; //报错说非法的前向引用
}
static BB a = new BB() ;
public staic void main(String args[])
{
CC c = new CC() ;
}
}为什么我在static代码块中对a进行了初始化,仍然报错呢?
原因就涉及了java对于初始化过程中对成员变量的限制:
成员变量a如果满足如下的4点,就必须在使用前必须对该成员变量进行声明
设定C为直接包含该成员变量的类或者接口
如果a出现在在C的或静态成员/非静态成员初始化 或者 C的静态或非静态代码块中
如果a不是 一个赋值不等式的左值
通过简单名称来访问
在我自己写的代码中,a.printA() ;出现的位置是CC的静态代码块中,通过简单名称直接访问(也就是直接使用a), 并且不是赋值不等式的左值,所以会报错“非法的前向引用”
这个是java语言规范中的原文代码(其中的中文是我自己的标注):
class UseBeforeDeclaration
{
static
{
x = 100;
// ok - assignment , 赋值表达式的左值
int y = x + 1;
// error - read before declaration , 赋值表达式的右值
int v = x = 3;
// ok - x at left hand side of assignment , 左值
int z = UseBeforeDeclaration.x * 2;
// ok - not accessed via simple name , 是通过类.静态变量 的形式访问, 而非直接简单访问
Object o = new Object()
{
void foo()
{
x++;
}
// ok - occurs in a different class , 不是CC的代码块或成员初始化中,而是在一个全新的内部类的函数中
{
x++;
}
// ok - occurs in a different class , 在一个内部类的代码块中, 和上一个类似
};
}
{
j = 200;
// ok - assignment
j = j + 1;
// error - right hand side reads before declaration , 第二个右值
int k = j = j + 1;
// error - illegal forward reference to j , 第三个是右值
int n = j = 300;
// ok - j at left hand side of assignment , 左值
int h = j++;
// error - read before declaration , 右值, 并参与了自增运算
int l = this.j * 3;
// ok - not accessed via simple name 通过this.j进行访问, 非直接简单访问
Object o = new Object()
{
void foo()
{
j++;
}
// ok - occurs in a different class
{
j = j + 1;
}
// ok - occurs in a different class
};
}
int w = x = 3;
// ok - x at left hand side of assignment
int p = x;
// ok - instance initializers may access static fields
static int u =
(new Object()
{
int bar()
{
return x;
}
}).bar();
// ok - occurs in a different class
static int x;
int m = j = 4;
// ok - j at left hand side of assignment
int o =
(new Object()
{
int bar()
{
return j;
}
}).bar();
// ok - occurs in a different class
int j;
}非法向前引用的例子:
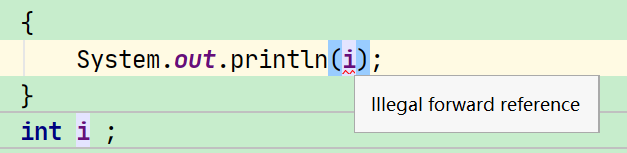
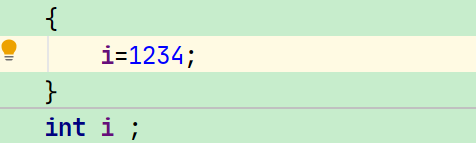
那么为什么类似于i= "1234";这样的代码可以呢?
这是因为Java对其中的某些情况做了“特许”,其中有一条就是“通过简单名称引用的变量可以出现在左值位置,但不能出现在右值的位置”,所以前面的代码可以,但System.out.println(i);不行,因为这是一个右值引用。
其目的是避免循环初始化和其他非正常的初始化行为。
什么是循环引用,看一下下面这个例子:
privateinti=j; privateintj=i;
如果没有前面说的强制检查,那么这两句代码就会通过编译,但是很容易就能看得出来,i和j并没有被真正赋值,因为两个变量都是未初始化的(Java规定所有变量在使用之前必须被初始化)





