Springboot国际化可以帮助使用者在不同语言环境中构建应用程序,这样应用程序可以有效地适应不同语言文化背景下的用户需求。
此外,Springboot国际化也可以方便多语言应用程序重用和维护,从而减少了系统部署的时间成本和维护的费用。
要实现Springboot国际化应用,主要有三个步骤。
定义国际化资源文件,使用properties格式的文件,将不同的多国语言文本资源放在不同的文件中,每个文件的命名采用【locale】+【messages】的方式,如zh_CN.properties、en_US.properties等。
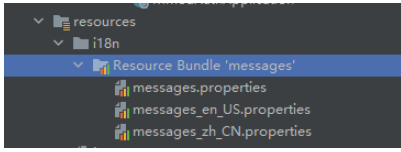
message.properties文件内容可为空。
message.en_US.properties内容示例:
40001=Hello
message.zh_CN.properties内容示例:
40001=你好
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.InterceptorRegistry;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.WebMvcConfigurer;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.i18n.LocaleChangeInterceptor;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.i18n.SessionLocaleResolver;
import java.util.Locale;
@Configuration
public class LocaleConfig {
@Bean
public SessionLocaleResolver localeResolver() {
SessionLocaleResolver localeResolver = new SessionLocaleResolver();
localeResolver.setDefaultLocale(Locale.CHINA);
return localeResolver;
}
@Bean
public WebMvcConfigurer localeInterceptor() {
return new WebMvcConfigurer() {
@Override
public void addInterceptors(InterceptorRegistry registry) {
LocaleChangeInterceptor localeInterceptor = new LocaleChangeInterceptor();
localeInterceptor.setParamName("lang");
registry.addInterceptor(localeInterceptor);
}
};
}
}application.properties中添加如下内容
#i18n spring.messages.basename=i18n.messages spring.messages.cache-duration=3600 spring.messages.encoding=UTF-8
application.yml中添加如下内容
spring: messages: basename: i18n/messages
Springboot的国际化是通过一个称为“messageSource”的bean实现的。
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.context.MessageSource;
import org.springframework.context.i18n.LocaleContextHolder;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.CrossOrigin;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/test")
public class TestControler {
@Autowired
private MessageSource messageSource;
@GetMapping("/hello")
public Map<Object, Object> test() {
Map<Object, Object> result = new HashMap<Object, Object>();
result.put("code", 40001);
result.put("msg", messageSource.getMessage("40001", null, LocaleContextHolder.getLocale()));
return result;
}
}Springboot国际化可以帮助使用者在不同语言环境中构建应用程序,这样应用程序可以有效地适应不同语言文化背景下的用户需求。
此外,Springboot国际化也可以方便多语言应用程序重用和维护,从而减少了系统部署的时间成本和维护的费用。要实现Springboot国际化应用,主要有三个步骤。
1.设置国际化属性文件:要实现Springboot国际化,首先要准备一系列国际化属性文件,包括语言和地区信息。
2.注册国际化消息资源:将属性文件中的语言和地区信息注册到Springboot应用程序中,并指定默认值,以便在扩展多语言时可以快速、高效地访问相关属性资源。
3.定义多语言捆绑文件:将已定义的国际化属性文件与应用程序结合起来,形成多语言捆绑文件,以便在用户选择不同语言时可以及时调整应用程序语言版本。





