多维数组(矩阵ndarray)
ndarray的基本属性
shape维度的大小ndim维度的个数dtype数据类型1.1.1 rand
生成指定维度的随机多维度浮点型数组,区间范围是[0,1)
Random values in a given shape.
Create an array of the given shape and populate it with
random samples from a uniform distribution
over ``[0, 1)``.
nd1 = np.random.rand(1,1)
print(nd1)
print('维度的个数',nd1.ndim)
print('维度的大小',nd1.shape)
print('数据类型',nd1.dtype) # float 64
1.1.2 uniform
def uniform(low=0.0, high=1.0, size=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
"""
uniform(low=0.0, high=1.0, size=None)
Draw samples from a uniform distribution.
Samples are uniformly distributed over the half-open interval
``[low, high)`` (includes low, but excludes high). In other words,
any value within the given interval is equally likely to be drawn
by `uniform`.
Parameters
----------
low : float or array_like of floats, optional
Lower boundary of the output interval. All values generated will be
greater than or equal to low. The default value is 0.
high : float or array_like of floats
Upper boundary of the output interval. All values generated will be
less than high. The default value is 1.0.
size : int or tuple of ints, optional
Output shape. If the given shape is, e.g., ``(m, n, k)``, then
``m * n * k`` samples are drawn. If size is ``None`` (default),
a single value is returned if ``low`` and ``high`` are both scalars.
Otherwise, ``np.broadcast(low, high).size`` samples are drawn.
Returns
-------
out : ndarray or scalar
Drawn samples from the parameterized uniform distribution.
See Also
--------
randint : Discrete uniform distribution, yielding integers.
random_integers : Discrete uniform distribution over the closed
interval ``[low, high]``.
random_sample : Floats uniformly distributed over ``[0, 1)``.
random : Alias for `random_sample`.
rand : Convenience function that accepts dimensions as input, e.g.,
``rand(2,2)`` would generate a 2-by-2 array of floats,
uniformly distributed over ``[0, 1)``.
Notes
-----
The probability density function of the uniform distribution is
.. math:: p(x) = \frac{1}{b - a}
anywhere within the interval ``[a, b)``, and zero elsewhere.
When ``high`` == ``low``, values of ``low`` will be returned.
If ``high`` < ``low``, the results are officially undefined
and may eventually raise an error, i.e. do not rely on this
function to behave when passed arguments satisfying that
inequality condition.
Examples
--------
Draw samples from the distribution:
>>> s = np.random.uniform(-1,0,1000)
All values are within the given interval:
>>> np.all(s >= -1)
True
>>> np.all(s < 0)
True
Display the histogram of the samples, along with the
probability density function:
>>> import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
>>> count, bins, ignored = plt.hist(s, 15, density=True)
>>> plt.plot(bins, np.ones_like(bins), linewidth=2, color='r')
>>> plt.show()
"""
pass
nd2 = np.random.uniform(-1,5,size = (2,3))
print(nd2)
print('维度的个数',nd2.ndim)
print('维度的大小',nd2.shape)
print('数据类型',nd2.dtype)
运行结果:

1.1.3 randint
def randint(low, high=None, size=None, dtype='l'): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
"""
randint(low, high=None, size=None, dtype='l')
Return random integers from `low` (inclusive) to `high` (exclusive).
Return random integers from the "discrete uniform" distribution of
the specified dtype in the "half-open" interval [`low`, `high`). If
`high` is None (the default), then results are from [0, `low`).
Parameters
----------
low : int
Lowest (signed) integer to be drawn from the distribution (unless
``high=None``, in which case this parameter is one above the
*highest* such integer).
high : int, optional
If provided, one above the largest (signed) integer to be drawn
from the distribution (see above for behavior if ``high=None``).
size : int or tuple of ints, optional
Output shape. If the given shape is, e.g., ``(m, n, k)``, then
``m * n * k`` samples are drawn. Default is None, in which case a
single value is returned.
dtype : dtype, optional
Desired dtype of the result. All dtypes are determined by their
name, i.e., 'int64', 'int', etc, so byteorder is not available
and a specific precision may have different C types depending
on the platform. The default value is 'np.int'.
.. versionadded:: 1.11.0
Returns
-------
out : int or ndarray of ints
`size`-shaped array of random integers from the appropriate
distribution, or a single such random int if `size` not provided.
See Also
--------
random.random_integers : similar to `randint`, only for the closed
interval [`low`, `high`], and 1 is the lowest value if `high` is
omitted. In particular, this other one is the one to use to generate
uniformly distributed discrete non-integers.
Examples
--------
>>> np.random.randint(2, size=10)
array([1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0])
>>> np.random.randint(1, size=10)
array([0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0])
Generate a 2 x 4 array of ints between 0 and 4, inclusive:
>>> np.random.randint(5, size=(2, 4))
array([[4, 0, 2, 1],
[3, 2, 2, 0]])
"""
pass
nd3 = np.random.randint(1,20,size=(3,4))
print(nd3)
print('维度的个数',nd3.ndim)
print('维度的大小',nd3.shape)
print('数据类型',nd3.dtype)
展示:
[[11 17 5 6]
[17 1 12 2]
[13 9 10 16]]
维度的个数 2
维度的大小 (3, 4)
数据类型 int32
注意点:
1、如果没有指定最大值,只是指定了最小值,范围是[0,最小值)
2、如果有最小值,也有最大值,范围为[最小值,最大值)
1.2.1 array
通过列表进行创建 nd4 = np.array([1,2,3]) 展示: [1 2 3] 通过列表嵌套列表创建 nd5 = np.array([[1,2,3],[4,5]]) 展示: [list([1, 2, 3]) list([4, 5])] 综合 nd4 = np.array([1,2,3]) print(nd4) print(nd4.ndim) print(nd4.shape) print(nd4.dtype) nd5 = np.array([[1,2,3],[4,5,6]]) print(nd5) print(nd5.ndim) print(nd5.shape) print(nd5.dtype) 展示: [1 2 3] 1 (3,) int32 [[1 2 3] [4 5 6]] 2 (2, 3) int32
1.2.2 zeros
nd6 = np.zeros((4,4)) print(nd6) 展示: [[0. 0. 0. 0.] [0. 0. 0. 0.] [0. 0. 0. 0.] [0. 0. 0. 0.]] 注意点: 1、创建的数里面的数据为0 2、默认的数据类型是float 3、可以指定其他的数据类型
1.2.3 ones
nd7 = np.ones((4,4)) print(nd7) 展示: [[1. 1. 1. 1.] [1. 1. 1. 1.] [1. 1. 1. 1.] [1. 1. 1. 1.]]
1.2.4 arange
nd8 = np.arange(10) print(nd8) nd9 = np.arange(1,10) print(nd9) nd10 = np.arange(1,10,2) print(nd10)
结果:
[0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9]
[1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9]
[1 3 5 7 9]
注意点:
nd11 = np.arange(10) print(nd11) nd12 = nd11.reshape(2,5) print(nd12) print(nd11) 展示: [0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9] [[0 1 2 3 4] [5 6 7 8 9]] [0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9] 注意点: 1、有返回值,返回新的数组,原始数组不受影响 2、进行维度大小的设置过程中,要注意数据的个数,注意元素的个数 nd13 = np.arange(10) print(nd13) nd14 = np.random.shuffle(nd13) print(nd14) print(nd13) 展示: [0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9] None [8 2 6 7 9 3 5 1 0 4] 注意点: 1、在原始数据集上做的操作 2、将原始数组的元素进行重新排列,打乱顺序 3、shuffle这个是没有返回值的
两个可以配合使用,先打乱,在重新排列
nd15 = np.arange(10,dtype=np.int64) print(nd15) nd16 = nd15.astype(np.float64) print(nd16) print(nd15) 展示: [0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9] [0. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9.] [0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9] 注意点: 1、astype()不在原始数组做操作,有返回值,返回的是更改数据类型的新数组 2、在创建新数组的过程中,有dtype参数进行指定
arr1 = np.arange(10) # 数组转列表 print(list(arr1)) print(arr1.tolist()) 展示: [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9] [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]
x = np.zeros(shape=[10, 1000, 1000], dtype='int')
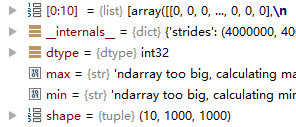
得到全零的多维数组。
x[*,*,*] = ***
np.save("./**.npy",x)
x = np.load("path")





