通过自定义需要整理的文件目录,将该目录下面的全部文件按照文件格式完成分类操作。
实现逻辑使用的python技术栈就是os、glob、shutil三个标准库的综合运用,完成自动化的文件整理。
分别将这三个文件处理模块导入代码块中,进入后续的开发操作。
# It imports the os module. import os # Shutil is a module that provides a number of high-level operations on files and collections of files. import shutil # The glob module finds all the pathnames matching a specified pattern according to the rules used by the Unix shell, # although results are returned in arbitrary order. No tilde expansion is done, but *, ?, and character ranges expressed # with [] will be correctly matched. import glob import sys
将需要分类的文件目录uncatched_dir以及分类后文件存放目录target_dir设置为可以手动输入的方式。
# Asking the user to input the path of the directory that contains the files to be sorted.
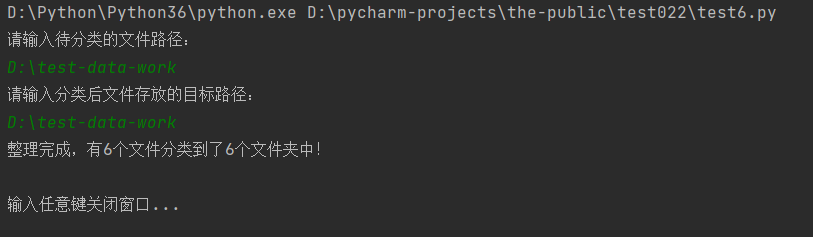
uncatched_dir = input('请输入待分类的文件路径:\n')
# It checks if the uncatched_dir is empty.
if uncatched_dir.strip() == '':
print('待分类的文件夹路径不能为空!')
sys.exit()
# Asking the user to input the path of the directory that contains the files to be sorted.
target_dir = input('请输入分类后文件存放的目标路径:\n')
# It checks if the target_dir is empty.
if target_dir.strip() == '':
print('分类后的文件存放路径不能为空!')
sys.exit()
检验输入的分类后文件存放目录路径是否存在,因为很可能是输入一个新的路径,不存在时则新建一个该路径。
# It checks if the target_dir exists. If it does not exist, it creates a new directory in the current working directory. if not os.path.exists(target_dir): # It creates a new directory in the current working directory. os.mkdir(target_dir)
定义一个文件移动数量的变量file_move_num,以及一个新建的文件夹数量的变量dir_new_num用于记录文件整理的结果记录。
# A variable that is used to count the number of files that have been moved. file_move_num = 0 # A variable that is used to count the number of new directories that have been created. dir_new_num = 0
遍历需要整理的文件夹目录uncatched_dir,对该目录下面的所有类型的文件进行自动整理操作。
# A for loop that iterates through all the files in the uncatched_dir directory.
for file_ in glob.glob(f'{uncatched_dir}/**/*', recursive=True):
# It checks if the file is a file.
if os.path.isfile(file_):
# It gets the file name of the file.
file_name = os.path.basename(file_)
# Checking if the file name contains a period.
if '.' in file_name:
# Getting the suffix of the file.
suffix_name = file_name.split('.')[-1]
else:
# Used to classify files that do not have a suffix.
suffix_name = 'others'
# It checks if the directory exists. If it does not exist, it creates a new directory in the current working
# directory.
if not os.path.exists(f'{target_dir}/{suffix_name}'):
# It creates a new directory in the current working directory.
os.mkdir(f'{target_dir}/{suffix_name}')
# Adding 1 to the variable dir_new_num.
dir_new_num += 1
# It copies the file to the target directory.
shutil.copy(file_, f'{target_dir}/{suffix_name}')
# Adding 1 to the variable file_move_num.
file_move_num += 1注意:为了避免移动文件夹而造成的异常,尤其是系统盘,因此这里用的是复制,也就是shutil.copy函数使用。
最后,将文件分类数量、文件夹新建数量使用print函数进行打印即可。
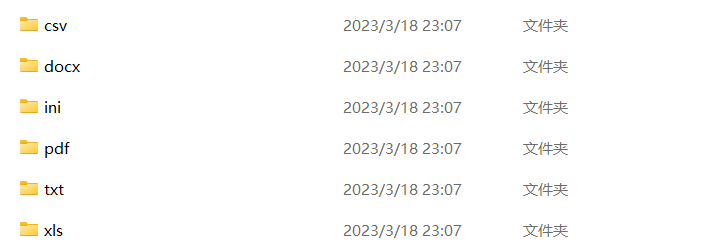
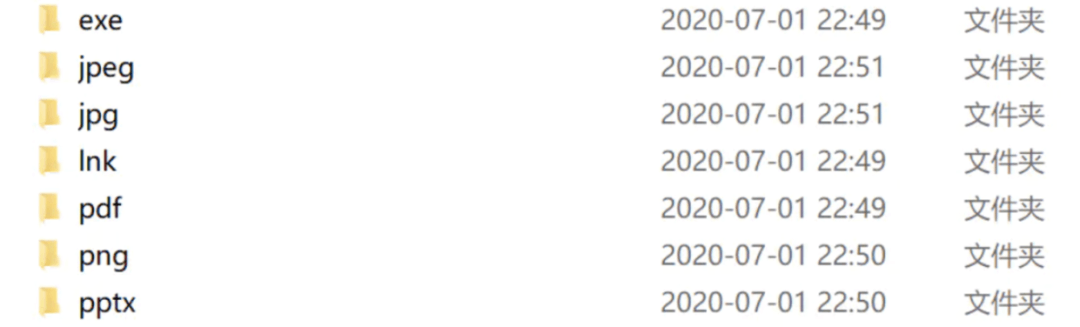
print(f'整理完成,有{file_move_num}个文件分类到了{dir_new_num}个文件夹中!\n')
input('输入任意键关闭窗口...')为了避免程序执行完成后直接将命令窗口关闭,上面使用了input函数来保持窗口暂停的效果。