数据结构是以结构化方式组织的数据集合。它分为两种类型,即线性数据结构和非线性数据结构。
线性数据结构 - 在这里,数据以线性方式组织。
例如 - 数组、结构体、栈、队列、链表。
非线性数据结构 - 在这里,数据以层次结构方式组织。
例如 - 树、图、集合、表格。
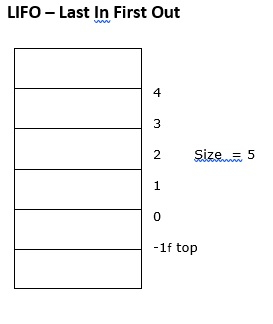
它是一种线性数据结构,数据只能在一端插入和删除。

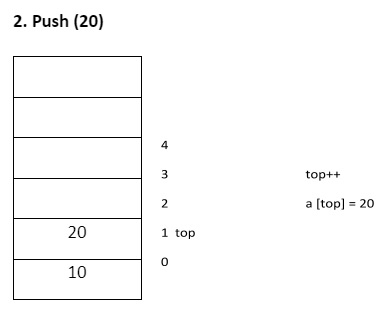

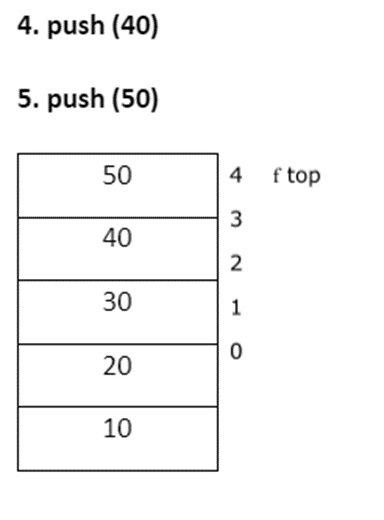
Deleted element = 50 Item = a [top] top --
Deleted element = 40 Deleted element=30 Deleted element=20 Deleted element =10
堆栈溢出
堆栈溢出 - 尝试向满栈插入元素。
堆栈下溢 - 尝试从空栈中删除元素。
相应的算法如下:
if (top = = n-1)
printf("stack over flow”);top ++ a[top] = item
if ( top = = -1) printf( "stack under flow”);
item = a[top] top --
if (top == -1)
printf ("stack is empty”);for (i=0; i<top; i++)
printf ("%d”, a[i]);以下是使用数组实现堆栈的C程序:
#include<stdio.h>
#include <conio.h>
int top = -1, n,a[100];
main ( ){
int ch;
void pop ( );
void display ( );
clrscr ( );
printf ("enter the size of the stack”);
scanf ("%d”, &n);
printf("stack implementation”);
printf ("1. push
”);
printf ("2. Pop
”);
printf ("3. exit
”);
do{
printf ( "enter ur choice”);
scanf ("%d”, &ch);
switch (ch){
case 1 : push ( );
display ( );
break;
case 2 : push ( );
display ( );
break;
case 3 : exit
}
}while (ch>=1 | | ch<= 3);
getch ( );
}
void push ( ){
int item;
if (top = = n-1)
printf ( "stack over flow”)
else{
printf("enter an element for insertion”)
scanf ("%d”, &item);
top ++;
a[top] = item;
}
}
void pop ( ){
int item;
if (top = = -1);
printf ( "stack under flow”);
else{
item = a[top];
top --;
printf("deleted element = %d”, item);
}
}
void display ( ){
int i;
if (top = = -1)
printf ( "stack is empty”);
else{
printf("contents of the stack are”);
for (i=0; i<top; i++)
printf ("%d t”, a[i]);
}
}
当执行上述程序时,它会产生以下结果 −
enter the size of the stack = 5 [given by user] Stack implementation 1. Push 2. Pop 3. exit Enter ur choice : 1 [given by user] Enter an element for insertion : 10 Contents of the stack : 10 Enter ur choice : 1 Enter an element for insertion : 2 Contents of the stack : 10 20 Enter ur choice : 2 Deleted element = 20 Contents of the stack are : 10 Enter ur choice : 2 Deleted element : 10 Contents of the stack are : stack is empty Enter ur choice : 2 Stack underflow. Enter ur choice : 1 Enter an element for insertion : 30 Contents of the stack are : 30





